Open ports are an essential component of modern networks. They enable communication between different devices and allow for the exchange of data. However, open ports also present a significant security risk, as they can be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your network.
In this article, we will delve into the risks associated with open ports and provide practical solutions for securing your network.
What are Open Ports and How Do They Work?
Open ports are network connection points that are open to receive incoming traffic. They are created when a program or service opens a socket and listens for incoming connections. Open ports allow for communication between different devices and allow for the exchange of data.
Why are Open Ports a Security Concern?
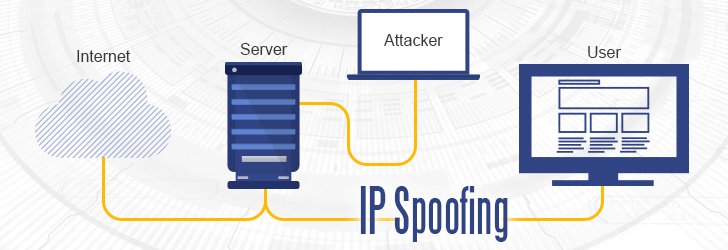
Open ports represent a security risk because they can be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your network. Unsecured open ports can be used to launch attacks, spread malware, steal sensitive information, and even compromise entire systems.
Identifying Open Ports on Your Network
To secure open ports on your network, it is essential to first identify which ports are open. There are several tools available for identifying open ports, including network scanners, port scanners, and vulnerability assessments.
Methods of Securing Open Ports
Once you have identified open ports on your network, there are several methods for securing them, including:
- Closing unneeded ports: If a port is not being used, close it to eliminate the risk of attack.
- Limiting access: Limit access to open ports by only allowing trusted sources to connect.
- Using firewalls: Implement a firewall to block incoming traffic from unknown sources and prevent unauthorized access.
- Enabling port security: Enable port security on switches to limit the number of MAC addresses that can connect to a port.
Best Practices for Open Port Vulnerability Assessment
In order to effectively secure open ports, it is essential to conduct regular vulnerability assessments. Some best practices for open port vulnerability assessment include:
- Regularly scanning your network for open ports.
- Keeping software and systems up to date.
- Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems.
- Monitoring logs and alerts for suspicious activity.
Implementing Mitigation Strategies for Open Ports
There are several strategies for mitigating the risks associated with open ports, including:
- Using firewalls to block incoming traffic from unknown sources.
- Limiting access to open ports by only allowing trusted sources to connect.
- Closing unneeded ports.
- Enabling port security to limit the number of MAC addresses that can connect to a port.
Case Studies:
Real-World Examples of Open Port Attacks To illustrate the real-world impact of open port attacks, we will examine several case studies. These case studies will demonstrate the consequences of unsecured open ports and highlight the importance of securing them.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, open ports can be both a blessing and a curse for network security. On the one hand, they allow for communication and connectivity, but on the other hand, they can also be a potential vulnerability for cyber attacks. It is crucial for organizations to keep track of their open ports and ensure that they are properly secured to minimize the risk of security breaches. Regular vulnerability assessments, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems can help mitigate these risks, but it is still essential to stay vigilant and educate employees on good security practices. By doing so, organizations can prevent cyber criminals from exploiting open ports and keep their sensitive data and systems secure.